Index
- Introduction
- Getting Started
- Modeller
- Overview I Refactory Modeller
- Technical Staging Model
- Logical Validation Model
- Central Facts Model
- Generic Access Model
- Model Check
- Model Deployment
- Web-App
- Overview I Refactory Web App
- For Delivery Agreements
- For Deliveries
- For Model Deployment
- For Settings
- Server
- OAuth2-Server
- Releases
- I Refactory Server
- I Refactory Modeller
- Glossary
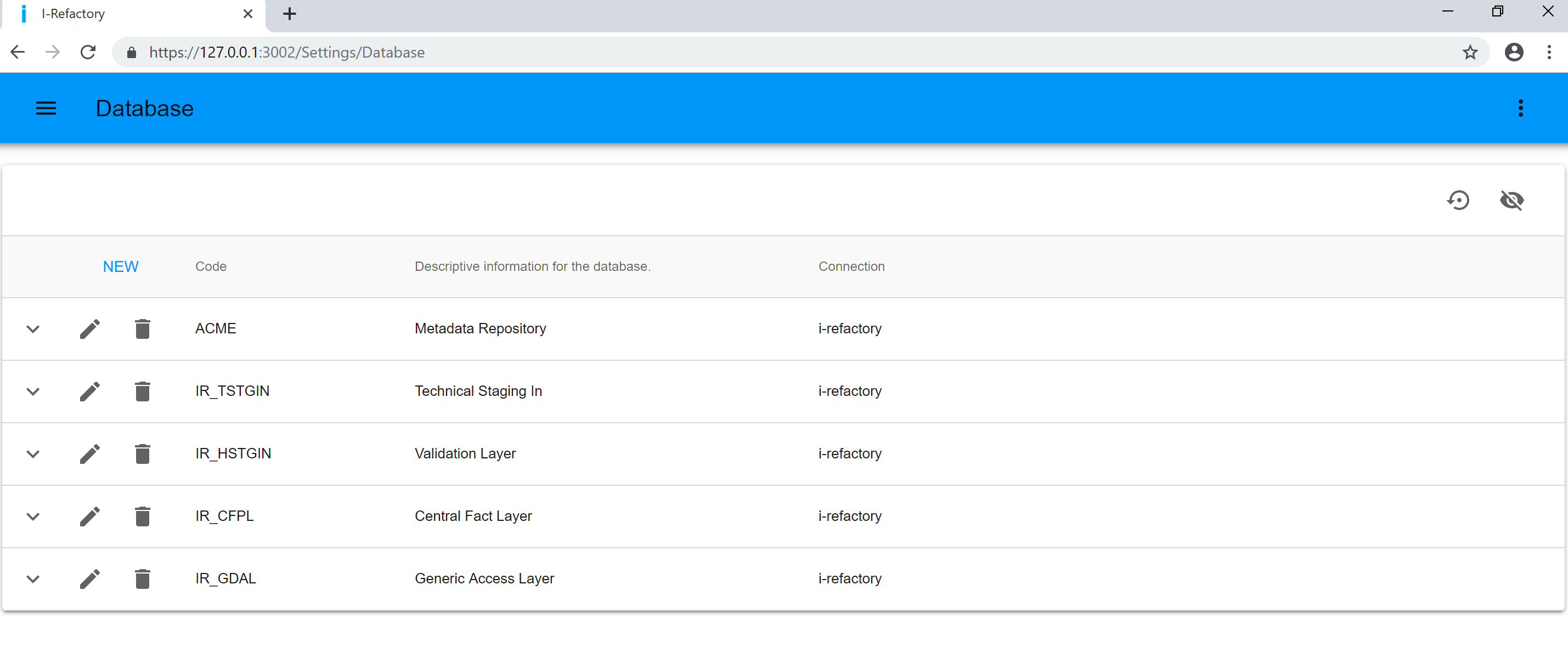
Configure Databases
In this section we explain how to configure the databases used by the i-refactory.
Configure a database
The databases used have to be configured in the i-refactory. For every layer a database has to be configured. The code represents the physical database name. This is used to define the connection used by the i-refactory application, and is used to validate the Design Time import.
- Go to menu : Settings > Databases
- Use the 'NEW' icon to create a new database
- Enter Code that represents the exact name your DBA has given to the database
- Enter a Description that describes the purpose of the database
- Select the Connection that formalizes the physical connection to this database
As an alternative you can also be configure Databases with the following API call : acmDatacon.database. An example of how to use this API can be found in S:\i-refact\i-refactory-engine\example\restful\createDatabase.js.
As part of our demo environment a possible list of databases is :
What's next?
- You can configure the connections
- Check the overview
Constraint violation actions are applicable to certain constraint categories. Not all combinations of constraint categories and violation actions are allowed.
An attribute must have a value, whatever that value may be. It must not be NULL.
A data type of an attribute defines what value an attribute can hold. The data type specifies what type of mathematical, relational, or logical operations can be applied to it without causing an error.
An attribute datatype constraint is the most basic constraint type. It checks for the datatypes we support and have implemented.
For example, we check for string, length of string, integer, date, etc. In the following figure you can see the supported data types by PowerDesigner.
Image is omitted: Supported data types
Constraints can be violated and there are some actions that can be performed when a violation occurs. The possible actions are: EMPTY COLUMN, NO ACTION and SKIP ROW.
An attribute value constraint is an expression that is evaluated. The person who writes the expression is responsible for the correctness of it. The expression should be formulated in a positive way and lead to a Boolean answer. If the expression validates to True, than the value is correct.
Examples
- The values in attribute X has to be bigger than 10:
X > 10 - The email address has to be in a certain pattern:
email address LIKE '%_@_%.__%'
A Concept Integration Model is also a central facts model on which you place integration patterns. It is not required to create a concept integration model, but it can be very useful.
Every constraint is assigned to a constraint classification.
The main purposes of the Generic Data Access Layer (GDAL) are to provide logical perspectives for data consumption and to manage CRUD actions.
A generic data access model is a virtual data model that acts as an interface bridge between consumer applications and the central fact storage.
Every attribute is assigned to an attribute classification.
An entity record constraint checks whether an attribute meets the requirements set by another attribute belonging to the same entity.
The main purpose of the Logical Validation Layer (LVL) is to transform the data received from external data sources to fit into the logical data model structure. It is also responsible for validating deliveries. The Logical Validation Layer is also known as the Historical Staging In (HSTGIN) Layer.
The logical validation model is the representation of a single external data source in a logical format. It represent how data delivered by a specific tenant should be transformed, temporalized and validated in the {popup}logical validation layer. The logical validation model is also known as Historical Staging model (HSTGIN).
Multi-active attributes are attributes that contain a business key to provide multiple context records at the same time. For example: a customer has multiple types of phone numbers. “Home”, “Work” and “Mobile”. In that case we add a dependent entity on customer with key “Phone Nbr Type”. This is to prepare for the CFPL multi-active key on customer.
The main purpose of the Technical Staging Layer (TSL) is to create a common starting point for further data processing. It receives data delivered from external data sources and temporally stores them in a database. The input data should be in a tabular format (rows and columns).
Bi-temporal attribute is an attribute that changes over time: they follow a valid timeline. For example, a Part may have a price valid for December and a price valid for January.
Every entity is assigned to an entity classification and to a parent entity classification. The possible values for entity classification are: ALTERNATE KEY CONTEXT, ATTRIBUTE CONTEXT, GENERALIZATION,HELPER, REFERENCE CONTEXT, STABLE, STABLE DEPENDENT and STABLE INDEPENDENT
Entity Set Constraint An entity set constraint can be used to perform a check concerning values of two or more attributes that belong to different entities or to perform a check concerning the value of an attribute with respect to a set of values.
A Set Constraint Helper is a helper in the logical validation model. It is the implementation of a set constraint. The helper returns the records of an entity for a given set constraint, where the instances of this entity do not meet the definition of this set constraint.
The business requirements describe how data should be delivered for the data consumers (end users or applications) in terms of concepts, relationships between concepts and constraints to validate the data. These requirements can be described in a logical data model, for example.
A Business Rule Helper is a helper in the central facts model. It is a set-based calculation of derived facts. You need to use a Business Rule Helper if you want to make a calculation and want to keep a transaction history of the results of this calculation. You use the existing entities from the central facts model as input. The results of the helper must be materialized in 'regular' fact entities, such as Anchors and Contexts, to make them accessible in the Generic Data Access Layer.
Closed Open means that the timeline is valid from (vanaf in Dutch) the supplied valid start date until - but not including - (tot in Dutch) the supplied valid end date. In practice, this means that the start date of a valid time record is equal to the end date of the previous valid time record.
You need to create context-based entities when a set of data may be delivered within the boundaries of a parent context. A context-based entity applies when:
- At least 2 entities are delivered.
- A context relationship exists between these 2 entities. One entity is the parent context of the other entity.
- The parent context entity is delivered as a delta and the child entity is delivered as a full set.
You need to create context-based entities when a set of data may be delivered within the boundaries of a parent context. A context-based entity applies when:
- At least 2 entities are delivered.
- A context relationship exists between these 2 entities. One entity is the parent context of the other entity.
- The parent context entity is delivered as a delta and the child entity is delivered as a full set.
The Management Model contains the PowerDesigner objects for the Unified Anchor Modelling (UAM). When a UAM object is created, a so-called PowerDesigner replica of the corresponding Management Model object is created. This means that certain properties such as metadata columns and column stereotypes are configured in the Management Model and cannot be changed. The replication settings specify which elements of an object can be changed after creating a replica from the template object. It is possible to override the replication settings of an UAM object and change a specific property.
The temporal atomic type describes the datatype of the temporal attributes|
The main purposes of the Central Facts Layer (CFL) is to store data historically. It can also integrate data from different sources. The Central Facts Layer is also known as Central Facts Persistency Layer (CFPL)
The central facts persistence implementation model is the representation of facts in an anchorized data model with the ability to integrate multiple logical models.
In the context of i-refactory, data transformation refers to operations involved in turning raw data readily useful and closer to the business requirements.
Integration patterns are used to integrate entities from different data models. If two or more entities from different data models share the same business key, you can use the Integration Pattern named Key Root. It is a good practice to capture integration patterns in a separate model, named Concept Integration Model.
An attribute is mandatory when its value can not be empty (NULL).
A Physical Data Model (PDM) represents how data will be implemented in a specific database.
{note} The i-refactory uses four PDMs: technical staging model, logical validation model, central facts model and generic access model. Each one of these models is implemented as an additional database, which is used to store data from external and internal data sources.
Reverse engineering is the process of reconstructing a physical and/or Entity Relationship (ER) model from an existing data source. The purpose of reverse engineering is to avoid manual work as much as possible.
Architecture layer
The core of the i-refactory architecture has four layers: TSTGIN, LVL, CFL and GDAL. There are also two auxiliary layers: UCLVL and EXT.
If an entity has one or more attributes that changes over time and you want to keep track of when a attribute is valid at a certain transaction time, then you have a special case of a regular dependent entity, called bi-temporal entity. The bi-temporal entity stores historical data with two timelines. The primary key of the bi-temporal entity is composed by the primary key of the parent entity and the valid start date attribute. The attribute that changes over the valid time is called a bi-temporal attribute.
If an entity has one or more attributes that changes over time and you want to keep track of when a attribute is valid at a certain transaction time, then you have a special case of a regular dependent entity, called bi-temporal entity. The bi-temporal entity stores historical data with two timelines. The primary key of the bi-temporal entity is composed by the primary key of the parent entity and the valid start date attribute. The attribute that changes over the valid time is called a bi-temporal attribute.
A delivery agreement is a contract between a Tenant and a Logical Implementation Model or Generic Data Access model. An agreement has a duration. The delivery agreement set the architecture layer (interface) where the data should be ingested as well as the default settings to be applied to the deliveries.
A dependency mapping is a mapping between a helper (or BR helper) and a source entity used in the query of the helper. The helper and the source entity must belong to the same model.
- Default dependency is set on entity level (source entity to helper entity)
- To allow lineage on attribute level, via the Mapping editor, you could manually add the dependency on attribute level.
An Independent Entity is an entity that implements an Anchor for a Business Key that ‘stands alone’ e.g. that does not contain a reference to another Entity.
An Independent Entity is an entity that implements an Anchor for a Business Key that ‘stands alone’ e.g. that does not contain a reference to another Entity.
A Logical Data Model (LDM) matches the language, structure and quality of the business, regardless of the physical data implementation. The Logical Data Model reflects the business requirements.
A delivery may be considered as "untrusted" if deletes of data in the Logical Validation Layer have taken place and the processing of new deliveries cannot 100% rely (trust) on having enough statistics and data available to detect logical deletes, to determine the exact delta and to execute set based validations.
A delivery may be considered as "untrusted" if deletes of data in the Logical Validation Layer have taken place and the processing of new deliveries cannot 100% rely (trust) on having enough statistics and data available to detect logical deletes, to determine the exact delta and to execute set based validations.
A Dependent Entity is an entity that implements an Anchor for a Business Key that ‘depends’ in its existence on another Entity. A Dependent Entity contains Business Key fields of which at least one is a foreign key (FK).
A Dependent Entity is an entity that implements an Anchor for a Business Key that ‘depends’ in its existence on another Entity. A Dependent Entity contains Business Key fields of which at least one is a foreign key (FK).
The transaction time in i-refactory is different from what is commonly understood by transaction time. Transaction time is usually seen as the moment when a fact was stored in the database. In the i-refactory, the transaction time is the time, as dictated by the source system, not by the i-refactory database.
The Attribute type links the attribute to one of the existing interfaces.
Computed columns are columns whose content is computed from values in other columns in the table.
Functional date A functional date or time is a point in time and is defined by a user. An example is an order date or date of birth.
The technical model (also known as Technical Staging In model: TSTGIN) is a representation of how exactly one delivery from a specific data source will be processed in the technical staging layer.
Generalization is the process of extracting shared characteristics from two or more classes (hyponyms), and combining them into a generalized superclass (hypernym). For example: an 'employee' and a 'customer' are both 'persons'.
The Mapping Editor provides a graphical interface for creating and viewing mappings between models. It provides a global view of all the mappings related to the entities of a given model, allowing you to quickly identify those which are mapped and not mapped.
When a certain fact can change over time and you need to capture when that fact is valid in the real world, you can add a valid start date and a valid end date to the entity.
A valid time tells us in which period a record is valid. While a functional date represents just one point in time, the valid time has a begin and an end date, for example:
- For Order item 123, a Retail price of 10.00 was valid from 2019-01-01 to 2019-06-01.
- For Order item 123, a Retail price of 12.00 was valid from 2019-06-01 to 2020-01-01.
Alternate key is an attribute or a group of attributes whose values uniquely identify every record in an entity, but which is not the primary key
Candidate key
A candidate key consists of one or more attributes and meets the following requirements:
- Unique: The value of the key defines uniquely one instance of a concepts. There are no double values.
- Non-volatile: (Almost) doesn't change.
- Minimal: Contains only the elements needed.
There are two kinds of candidate keys:
- primary key
- alternative key
A Key Root Link is an integration concept that must be used when the exact same business concept or dependent business key occurs in different models. The Links for this dependent business key in the different UAM models are all subtypes of the Keyroot Link.
Normalization is the process of decomposing tables in a database in order to reduce data redundancy and improve data integrity.
A strongly typed model is a model in which each all attributes have a predefined data type, for example: integers, doubles, date.
Surrogate Key A surrogate key is a system generated unique identifier that does not have any contextual or business meaning.
Business Key
A business key is an unique identifier that has business meaning and exists in the real world outside of the database. It consists of a column or a set of columns that already exists in a table. A business key is also known as a natural key
A Key Root Hub is an integration concept that must be used when the exact same business concept or independent business key occurs in different models. The Hubs for this independent business key in the different UAM models are all subtypes of the Keyroot Hub.
A relationship shows how two entities are related to one another. For example, a customer can place an order, and a order can have a customer.
Every Attribute has an atomic type (data type) which is linked to the attribute type of that attribute.
The cardinality shows how many instances of an entity can take place in a relationship.
The cardinality shows how many instances of an entity can take place in a relationship.
An enumeration consists of the list of values that a given attribute should adhere to.
{example} An order can have different statuses, such as shipped,packing,created anddone. Other statuses are not allowed.
Foreign Key
A foreign key is an attribute or a set of attributes that refers to the primary key of another entity. The original entity containing the primary key is called the 'parent' entity and the entity containing the foreign key is called the 'child' entity.
A natural key is an unique identifier that has business meaning and exists in the real world outside of the database. It consists of an column or a set of columns that already exists in a table. A natural key is also known as a business key
The primary key is an assigned key that consists of a minimal set of attributes to uniquely specify an instance of a record. The attribute or a combination of attributes should meet the following characteristics:
- Unique: The attribute values of the key uniquely identify one instance of a concept. There are no duplicate instances.
- Non-volatile: The key does not change.
- Mandatory: All values are filled; there are no NULL values.
It is good practice to choose a primary key that also meet the following characteristic:
- Safe: Doesn't contain private or sensitive information, such as a social security number.
Constraints are related to the other elements depending of the type of the constraint. Certain constraints are associated to attributes, entities, helper entities, unique keys or relationships between entities.
An attribute may be assigned to one or more entities (ex: acm_exists_ind) and an entity may have several attributes
Each layer may have one or more interfaces. The amount of interfaces depend on how many tenants and delivery agreements have been configured.
Namespace is what in the terminology of SQL Server is called database schema.|
A Delivery is a container that holds the specification of what is actually pushed to the i-refactory platform. This specification consists of a list of entities.
A Delivery is a container that holds the specification of what is actually pushed to the i-refactory platform. This specification consists of a list of entities.
Key Root A Key Root is a central repository for Business Keys. A Key Root ensures that similar records out of different data sources are identified by both the same Business Key as the Surrogated Key.
Context
A Context is a temporal table with a transaction start and end date. The Context tracks all changes of the context attributes related to a business key in the transaction time. This means that every change of an attribute value in a source system leads to a new record in the Context. The old record is end dated with the load date and the new record is start dated with the load date.
Hyponym is a term that denotes a subcategory of a more general class. For example: 'cat' and 'dog' are a hyponyms of 'animal'.
A mapping establishes relationships between concepts of separate data models. It creates a link between entities and attributes from a source model to related entities and attributes in the target model. A source model should precede the target model in the i-refactory architecture.
oasi_bk is an abbreviation for One Attribute Set Interface (OASI) with business keys. A normal view in the generic data access layer (GDAL) consists of the surrogate key, foreign key and attributes. The oasi_bk-view in the GDAL is a view where the business key(s) are also shown.
A subtype is a subgroup of an entity. You can create a subtype if a group of instances share some attributes and relationships that only exist for that group. For example, entity Customer can have a subtype Company and a subtype Person. They share the common attribute customer number, and can have some attributes of their own. Such as birth date for a Person. The entity Customer is called a supertype.
A subtype:
- inherits all attributes of the supertype
- inherits all relationships of the supertype
- usually has one or more own attributes
- can have subtypes of its own
Anchor: Independent Entity
An Independent Entity is an entity that implements an Anchor for a Business Key that ‘stands alone’ e.g. that does not contain a reference to another Entity.
Anchor: Dependent Entity
A Dependent Entity is an entity that implements an Anchor for a Business Key that ‘depends’ in its existence on another Entity.
A domain will help you to identify the types of information in your model. It defines the set of values for which a column is valid. A domain can specify a data type, length, precision, mandatoriness, check parameters, and business rules. It can be applied to multiple columns, which makes it easier to standardize data characteristics for columns in different tables.
Each interface may have one or more entities and one entity belongs to only one interface. An entity belongs to an i-refactory data model.
Each interface may have one or more entities and one entity belongs to only one interface. An entity belongs to an i-refactory data model.
A helper entity creates a derived entity and can be used when you need to transform, filter, or calculate data. The purpose of a helper differs per model:
- Technical model: a helper is used to transform data.
- Logical validation model: a helper is an implementation of a set constraint (Set Constraint Helper).
- Central facts model: a helper is used for a set-based calculation of derived facts (Business Rule Helper).
HSTGIN is the abbreviation of Historical STaging IN. It is an older term to indicate the Logical Validation Model or Logical Validation Layer.
A schema is a set of database objects, such as tables, views, triggers, stored procedures, etc. In some databases a schema is called a namespace. A schema always belongs to one database. However, a database may have one or multiple schema's. A database administrator (DBA) can set different user permissions for each schema.
Each database represents tables internally as <schema_name>.<table_name>, for example tpc_h.customer. A schema helps to distinguish between tables belonging to different data sources. For example, two tables in two schema's can share the same name: tpc_h.customer and complaints.customer.
A Tenant is a delivering party for a dataset or datarecord as agreed in the Delivery Agreement.
TSTGIN is the abbreviation of Technical STaging IN. It is an older term to indicate the Technical Model or Technical Staging Layer.
An index organizes data in a way that improves the speed of data retrieval from a database. To maintain the index data structure, there is a cost of additional writes and storage space.
An index organizes data in a way that improves the speed of data retrieval from a database. To maintain the index data structure, there is a cost of additional writes and storage space.
The acronym CRUD stands for create, read, update, and delete. These are the four basic functions of persistent storage.
OLAP is a acronym for Online Analytical Processing. OLAP is category of software tools which provide analysis of data for business decisions. It uses complex queries to analyze aggregated historical data from OLTP systems.The primary objective is data analysis and not data processing.
OLTP is a acronym for Online transaction processing. OLTP captures, stores, and processes data from transactions in real time. Its primary objective is data processing and not data analysis.
A hub or independent entity is an entity that implements an Anchor for a business key that ‘stands alone’ e.g. that does not contain a reference to another entity. An independent entity contains business key fields, that show up as alternate key (AK), and the primary key (PK) is its surrogate key (ID).
A key is a combination of one or more attributes of an entity that uniquely defines one instance of that entity.